Projects on Digital Business Development
From Digital to Smart Factory
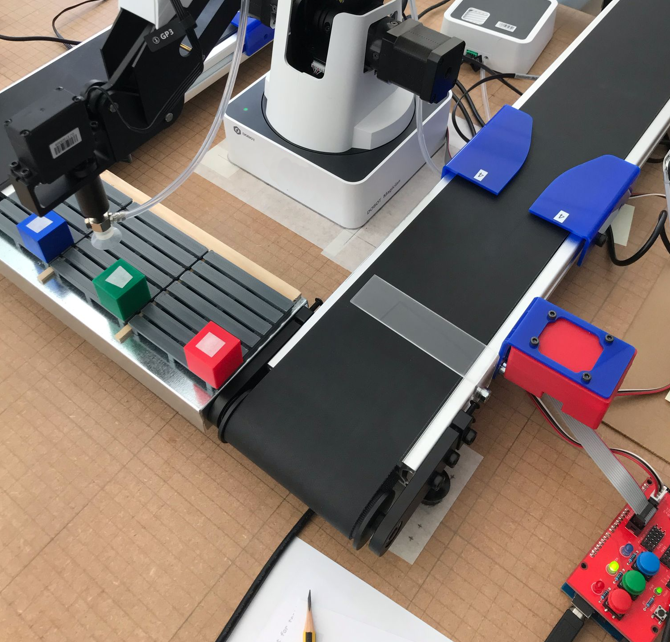
The Smart Factory project aims to explore how digitalisation can transform today’s digital factories into the smart factories of the future.
The project progresses through two steps:
Step 1: Identification and creation of the Digital Factory
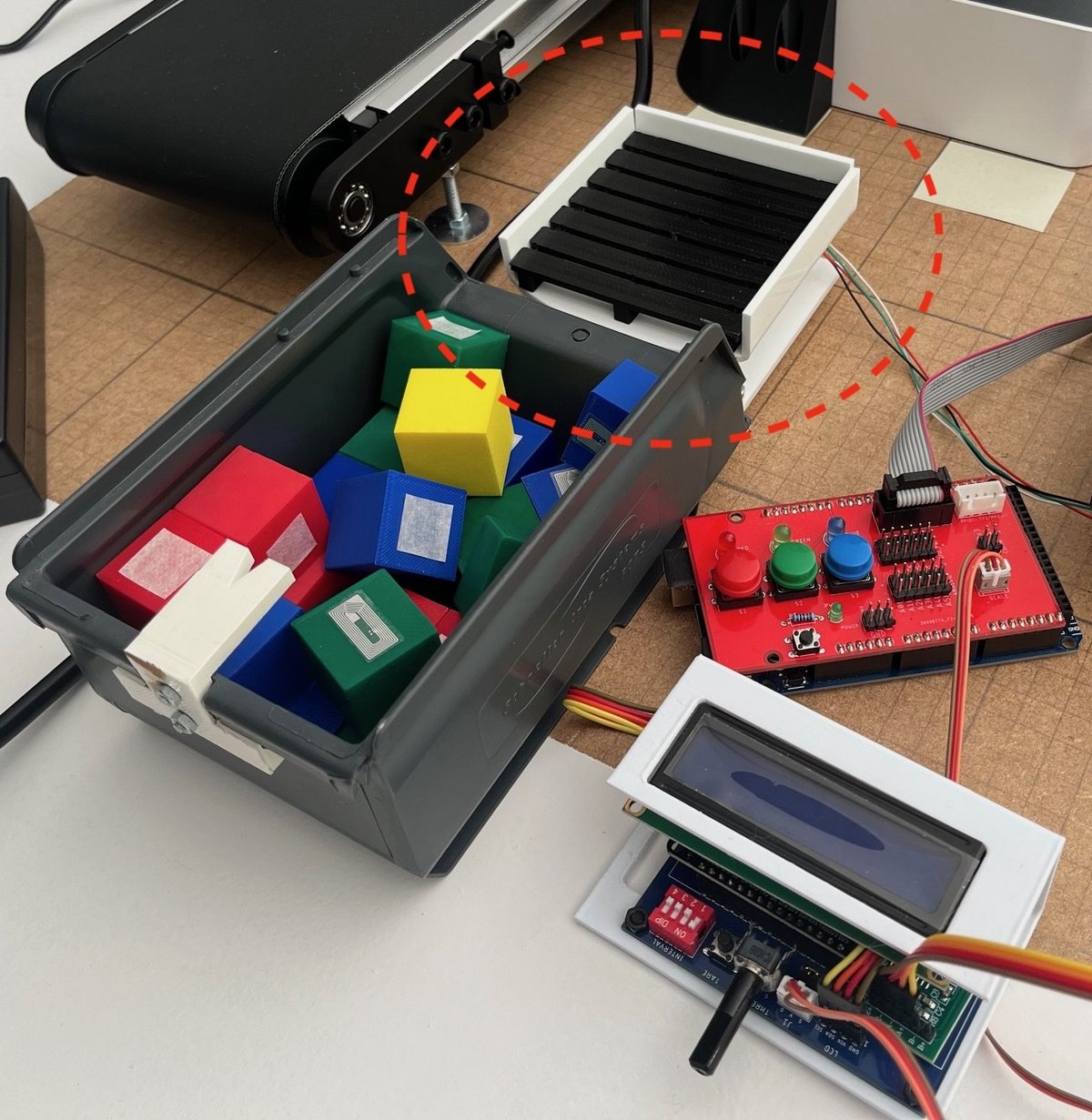
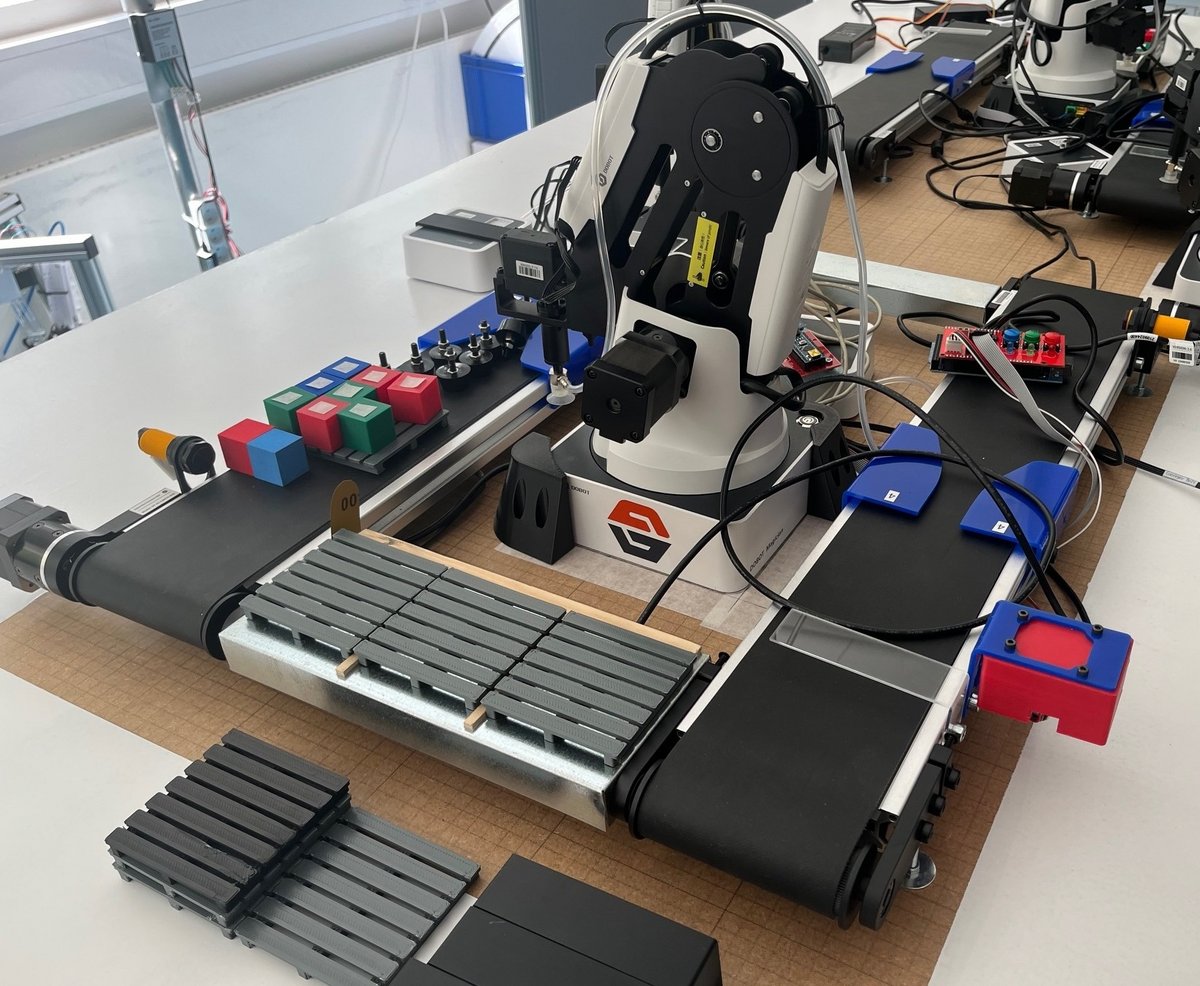
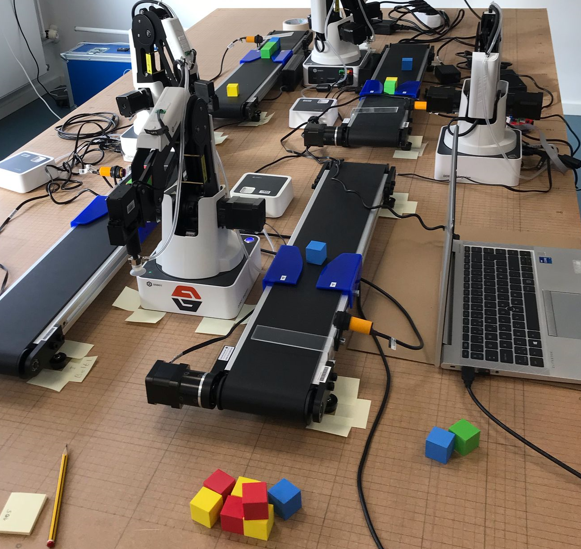
In this initial phase, the focus is on identifying and acquiring components to build a platform capable of simulating a digital factory. These components include equipment such as robots, conveyor belts, sensors, and RFID readers for identifying, sorting, and moving items. The goal of the Digital Factory is to create an automated production environment that supports teaching in automation and digitalisation (Industry 3.0).
Step 2: Transitioning from Digital Factory to Smart Factory
In this phase, the focus shifts to measuring, collecting, and visualising data, evolving the platform to simulate a smart factory. Building on the work initiated in Step 1, this phase leverages the existing infrastructure to create a self-contained system capable of making decisions based on input from devices, machines, external data, and commands, aiming to explore new processes, enhance productivity, and unlock research opportunities. The goal of the Smart Factory is to create an intelligent production environment that further advances teaching in automation and digitalisation by integrating principles from Industry 4.0 and IoT. This will enable students to test and demonstrate functionalities, gain data-driven insights, and explore remote control and advanced monitoring capabilities.
For now, the project is transitioning into the early phases of Step 2, with some elements of Step 1 still being refined.
Status 2025, August: The project, in its current form, has been concluded with support from IT-Vest. The system will be used for visitors and for demonstration and inspiration in teaching at AU BTECH. Future development will focus on implementing a vision system, along with wireless modules for data collection, remote monitoring, and communication between servers and stations – paving the way for IoT and Industry 4.0.
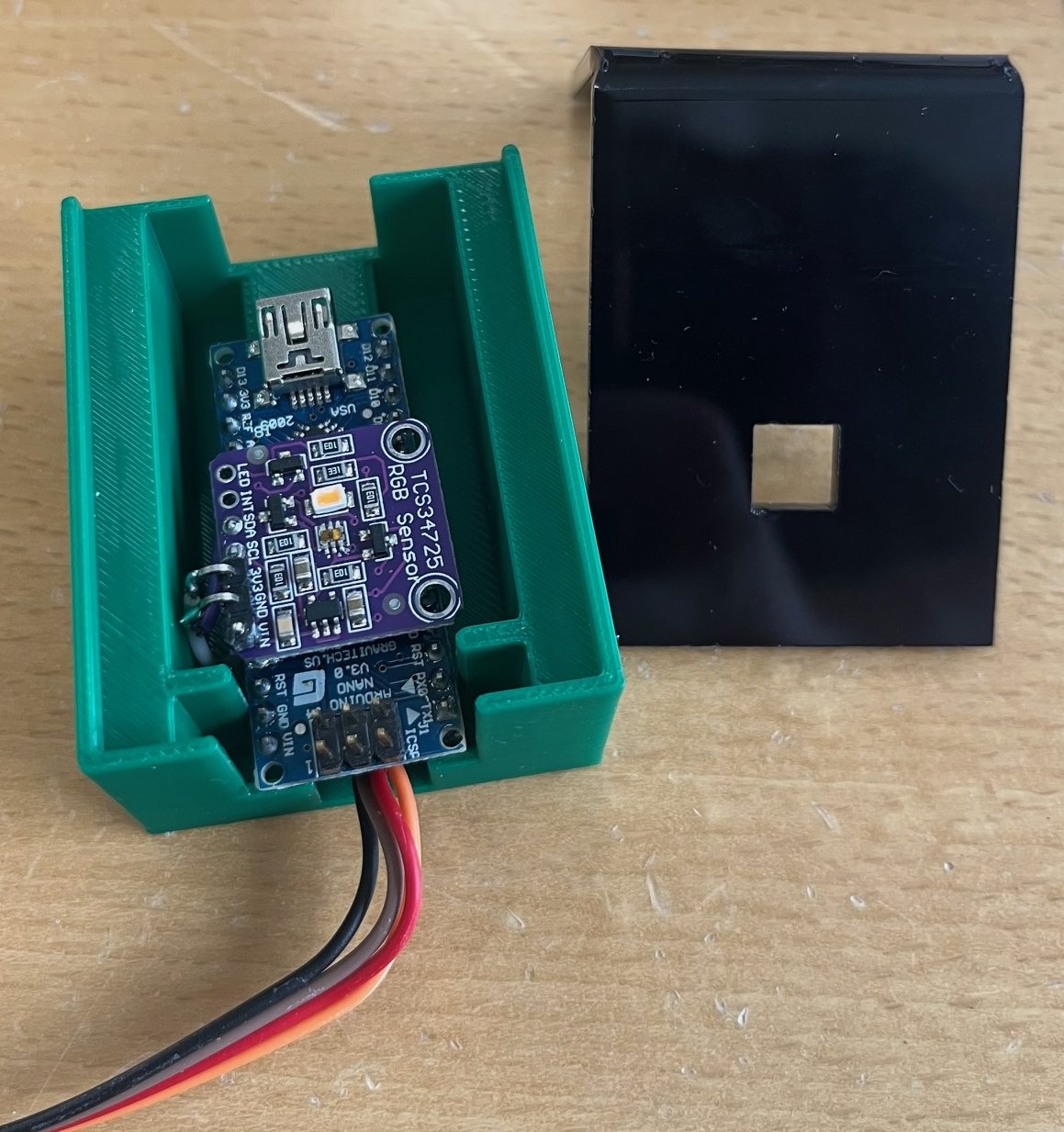
Status 2025, May: A color sensor (RGB sensor) has been developed, which can also be used to sort items. RFID technology can hold far more information than just color, but the color sensor has been selected as a complementary technology, particularly for sorting items.
Status 2025, April: A new phase of identifying and categorizing cubes (artifacts) using RFID tags has begun. Each cube has an RFID tag that stores data. For now, the data distinguishes each cube by color-code, but future updates will allow for differentiation based on unique characteristics – such as distinguishing blue cubes from each other.
Status 2025, March: The system has been expanded with a load cell (weighing scale). The load cells can be used to sort items based on their weight, but the primary use will be to identify whether a pallet is full or empty.
Status 2025, January: Initial testing and preliminary development of the physical setup is underway. The focus is on identifying the best possible layout that represents a streamlined production line with a focus on repeatability.
Project lead: Ulrich Bjerre.
The Use of AI in Project Management
The project aims to equip cand.it (ITKO*) students with the necessary skills and knowledge to apply AI tools and techniques in project management. This is achieved through teaching that fosters a deeper understanding of AI's role in modern project management methods and provides students with the competence to use AI in practical industrial contexts.
Organizations across industries recognize the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance project workflows, strengthen decision-making, and improve efficiency. By automating routine tasks and predicting risks, AI can transform how projects are planned, executed, and monitored. Given the growing demand for AI in project management practices, there is an increasing need to integrate AI concepts into the ITKO program. This will enable students to apply AI technologies in real-world project scenarios, preparing them for future roles as project managers, analysts, consultants, and leaders.
Project activities include interactive lectures, workshops, and discussions that will contribute to the development of teaching modules integrating AI concepts, tools, and techniques with project management principles. These teaching modules are expected to be included in the Project Management course within the ITKO program in both Aarhus and Herning.
*ITKO is a career-oriented and interdisciplinary education focused on integrating the core disciplines of IT, communication, and organization with the aim of shaping the digital integrators of the future.
Project lead: Maja Due Kadenic and Konstantinos Koumaditis.
Digital Responsibility and Digital Ethics for ITKO Students
The project aims to enhance the relevance of the cand.it (ITKO*) program in collaboration with external stakeholders from the labor market. This is achieved by developing students' competencies in digital responsibility and ethics.
In light of the technological acceleration, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI), there is a growing need for ITKO students to gain knowledge, skills, and competencies in digital responsibility and ethics. This will enable them to both develop and integrate AI and other digital technologies into products and services that create value for companies, organizations, and users, while ensuring that these innovations are grounded in responsible and ethical practices.
The project activities include a series of workshops with private companies and public organizations, aimed at producing teaching materials and case studies. These will be integrated into the Digital Communication course within the ITKO program in both Aarhus and Herning.
*ITKO is a career-oriented and interdisciplinary education focused on integrating the core disciplines of IT, communication, and organization with the aim of shaping the digital integrators of the future.
Project Lead: Anne Gammelgaard Ballantyne and Christiane Marie Høvring.
EXTERNAL PROJECTS
External DBD Project activities focus on promoting active learning and exploration of digital business development while contributing to alignment across research, teaching, and projects in the digital domain. The portfolio of external projects covers both research, development, and application projects in academia as well as in industry.
CompositeCircle | 2025–2028
The project aims to establish synchronized transnational value chains for the circularity of glass fibre-reinforced polymer composite products, pooling industry capacities across the region to create an economically viable recycling infrastructure.
This project is funded by the Interreg Baltic Sea Region, and the partner consortium consists of Riga Technical University, Lulea University of Technology, Podcomp AB, Hitachi Energy Sweden AB, Valmiera Municipality Government, and Aarhus University (DBD).
DBD contact: Michail Beliatis.

FOSS | 2024–2026
The Free Open-Source Software (FOSS) project explores how contributors organise within FOSS communities, both in physical and online spaces. This exploration has gained significant relevance, as research indicates that around 96% of all software has open-source components at its root. The aim of the project goal is to bridge industrial software development practices with FOSS organising practices, to enhance the quality and efficiency of the software supply chain overall.
This project is funded by AUFF Nova.
DBD contact: Mirko Presser.

Co-LIFE | 2023–2026
Co-LIFE is building a cross-continental network of educators, students, and stakeholders working toward a more inclusive and environmentally conscious economy. The project unites higher education institutions from Europe and India to co-develop innovative educational measures in impact-focused entrepreneurship
This project is funded by the EU, and the partner consortium consists of LAB University of Applied Sciences, Laurea University of Applied Sciences, Thomas More University of Applied Sciences, Arch College of Design & Business, Goa Institute of Management, Indian School of Development Management, and École Intuit Lab and Aarhus University (DBD). Read more about the Co-LIFE project here.
DBD contact: Eva Sørum Poulsen.

Cybersecure Production (CyPro) | 2022–2026
The CyPro project aims to strengthen the cybersecurity level of the Danish business sector in relation to the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0. The significance of IoT security as a strategic and commercial asset is accelerating in the digital age and has become more relevant to remain competitive than ever.
New knowledge, skills and concrete tools developed in the project will be made available to help Danish industrial companies to understand and utilise cybersecurity as a growth driver in production.
The project is funded by the Danish Industry Foundation, and the partner consortium consists of the Alexandra Institute, FORCE Technology, Ugla Insights, DAMRC and Aarhus University (DBD).
DBD contact: Anita Krogsøe Skou.
GlassCircle | 2022–2024
The GlassCircle project aims to explore a full cycle circular economy for the glass fiber industry. During glass fiber manufacturing, significant amount of residue material is generated that pollutes our environment, and creates additional costs, waste and inefficient material use within the glass fiber industry. By helping glass fiber manufacturers to develop business models for a morecircular economy, the project contributes to reducing the environmental impacts of glass fiber waste by bringing it back into use.
The project is funded by Interreg and the EU, and the partner consortium consists of Riga Technical University, Lulea University of Technology, Podcomp Ab, Hitachi Energy Sweden AB, Composites (HPAG), Valmiera Municipality Government and Aarhus University (DBD). Read more about the GlassCircle project here.
DBD contact: Michail Beliatis.
EINST4INE | 2021–2024
The EINST4INE projects aims to develop new concepts, approaches and methods in the area of industrial digital transformation. By looking through the individual, organizational and ecosystem perspectives, current digital transformation research gaps are addressed, leading to a new generation of Early Stage Researchers (ESRs) in innovation and technology management. The project strives to provide training and a knowledge-base in the areas of Open Innovation, Industry 4.0, digital transformation and innovation ecosystems.
The project is funded by the EU, and the partner consortium consists of University of Cambridge, LUT University, LUISS University, RMIT Europe, Sant’Anna School of Advanced Studies, University of Stuttgart and Aarhus University (DBD). Read more about the EinST4INE project here.
DBD contact: Agnieszka Radziwon.
NGI POINTER | 2020–2022
NGI POINTER is an open support programme aimed at reinventing the internet for the third millennium and beyond by cascading funding for promising bottom-up projects capable of building scalable protocols and tools to assist in the practical transition or migration to new or updated technologies.
The project is dedicated to supporting top internet researchers and innovators in addressing emerging technological opportunities. The project is funded by the EU, and the partner consortium consists of FundingBox, Digital Worx, Linknovate, and Aarhus University (DBD). Read more about the NGI POINTER project here.
DBD contact: Mirko Presser.
Digital Business Models for the Future | 2018-2020
Digital Business Models for the Future is a project aiming to develop and disseminate new knowledge and methods that will strengthen Danish manufacturing companies for a digital future.
Concrete tools and methods for developing and implementing digital business models are made freely accessible on the learning platform digitale-forretningsmodeller.dk. The project thus offers the industry to leverage the platform as a guide to becoming more competitive, adaptable and equipped for the future.
The project is funded by the Danish Industry Foundation, and the partner consortium consists of the Danish Technological Institute, Aarhus School of Marine and Technical Engineering, and Aarhus University (DBD). Find more information about the project here.
DBD contact: Anita Krogsøe Skou.
XR in Healthcare | 2025
XR in Healthcare is a project focussed on connecting training needs and technology opportunities in the healthcare sector. Training applications are deployed at Regionshospitalet Gødstrup to explore needs, requirements and opportunities for training healthcare professionals with the use of XR - Extended Reality (AR/VR/MR) technologies
This project is funded by AU Connect, and the partner consortium consists of Regionshospitalet Gødstrup and Aarhus University (DBD).
DBD contact: Konstantinos Koumaditis.

SENSIBLE | 2023–2027
SENSIBLE stands for Symbiotic tEleoperatioN for Safe and cost-efficient wInd turBine bLade maintEnance. The project aims to develop a robot that enables technicians to maintain wind turbines without having to climb up into them and rappel down along the wings.
This project is funded by the Innovation Fund, and the partner consortium consists of Clobotics, InnoPixel, University of Southern Denmark and Aarhus University (DBD).
DBD contact: Francesco Chinello.

Servitize | 2023–2025
The Servitize project is helping companies as they transform from a primary role as product suppliers to increasingly offering sustainable service concepts of the future. The aim is to make SMEs more internationally competitive by operationalising sustainable service concepts on an individual business level and creating more value—with digitalisation as a key tool.
This project is funded by the Danish Industry Foundation, and the partner consortium consists FORCE Technology, Danish Technological Institute, the Alexandra Institute, Danish Engineer's Association and Aarhus University (DBD). Read more about the Servitize project here.
DBD contact: René Chester Goduscheit & Dorte Borch Storper.

NGI Search | 2022-2025
NGI Search is an open support programme aimed at building a safer internet for end-users who are searching for information and resources on the internet. The project offers funding as well as technical, business and innovation support for the development of open-source technologies and solutions that are centred on privacy and trust.
This project is funded by the EU, and the partner consortium consists of Fundingbox, Linknovate, Murcia University, OW2 and Aarhus University (DBD). Read more about the NGI Search project here.
DBD contact: Mirko Presser.
Manufactory | 2022–2023
The Manufactory project aims to establish a growth technology centre that will build a bridge between knowledge and production and thus strengthen the competitiveness of the Danish manufacturing industry. The centre will support companies in increasing their innovative capacity and technological understanding by providing access to specialised knowledge and resources.
Manufactory unfolds in three phases 1. Pilot project, 2. Establishment, and 3. Operation. AU is leading the pilot project with activities such as testing project processes and new forms of collaboration between knowledge institutions and companies in the Midwest region, along with developing the strategic, economic and organisational plans for the centre.
The project is funded by the Danish Industry Foundation, and the partner consortium consists of Business Skive, Bæredygtig Herning, DAMRC, Danish Sound Cluster, Dansk AM Hub, Digital Transformation Lab, Herningsholm Erhvervsskole, Klimatorium, Lifestyle & Design Cluster, Aarhus University (Engineering and BSS represented by DBD) and 20 companies. Read more about the Manufactory project here.
DBD contact: Emilie Mathilde Jakobsen.
European Internet of Things (EU-IoT) | 2020–2023
In the current transition phase from Horizon 2020 to Horizon Europe, the EU-IoT project will provide a well-founded strategy and a cohesive plan of action for growing a sustainable and comprehensive ecosystem, which embraces several initiatives across the European IoT landscape in line with the Next Generation Internet (NGI) vision.
This project is funded by the EU, and the partner consortium consists of Aarhus University (DBD), Martel Innovate, INFRASOFT International, fortiss and BluSpecs. Read more about the EU-IoT project and the need for IoT consolidation here.
DBD contact: Emilie Mathilde Jakobsen.
Industrial Internet Playground (IIP) | 2019-2020
The IIP is part of the Industry 4.0 enablement programme and aims to boost digital maturity in industrial environments and propel manufacturing firms in the right direction to benefit from IoT technologies. The project deploys a radically new co-development concept for the introduction of digital technologies and digital processes in existing operations within various manufacturing industries to improve product quality, operations and machinery.
The IIP is also part of the EU-funded DIATOMIC initiative with the aim to establish a sustainable ecosystem for advanced microelectronics components and smart system integration innovations. This first IIP project, ‘Industry 4.0 – Living Lab for Acoustic Panel Production’, was led by the Belgian IoT startup PulseLabs, the Danish manufacturer of the acoustic panels Troldtekt and Aarhus University (DBD) as supporting knowledge centre. Read more about the IIP here.
DBD contact: Mirko Presser.
IoT Crawler | 2018-2020
The IoTCrawler project focuses on developing a search engine for the Internet of Things (IoT) with the aim of making real-world data from devices accessible and actionable, thus creating a smarter use across domains of data generated by IoT devices.
The project addresses dynamic search, discovery of IoT resources as well as security and privacy through the development of prototypes to demonstrate key IoT concepts in urban environments. The IoTCrawler results are used to develop new and advance existing intelligent services that will benefit citizens and decision makers.
This project is funded by the EU, and the partner consortium consists of Universidad de Murcia, University of Surrey, Osnabrück University of Applied Sciences, Siemens AG Österreich, NEC Corporation, AGT Group, Digital Worx, Odin Solutions S.L, Aarhus Municipality and Aarhus University (DBD). Find more information about the IoT Crawler project here.
DBD contact: Mirko Presser.
For further information on specific state-of-the-art technologies, business models or case studies associated with the presented projects, feel free to reach out to the DBD Project contact person listed for the project concerned.
We encourage industry partners, researchers and PhD students to reach out and propose potential collaboration projects in the domain of digital business development. Please contact Associate Professor and head of the DBD Project Martin Olsen for further information on the opportunities for joint projects.